Accumulator
介绍 Accumulator 之前,先了解下什么是 Merkle Tree。 在 Starcoin 中,Accumulator 可以认为是 Merkle Tree 存储在 KvStore 上。
用途
这颗树的作用主要是提供 Block,Transaction 的 Merkle Proof,以及通过指序列号获取对应的 Block(Transaction 类似)。 下面介绍下在 Starcoin 中 Accumulator 的一些信息。
节点类型介绍
节点分为三种类型 Leaf,Internal,Empty。 这里以存储 Block 为例子(存储 Transaction类似)。 图1显示了偶数个 Block 组成一个 Accumulator 的情况(这里只有 Leaf 和 Internal)
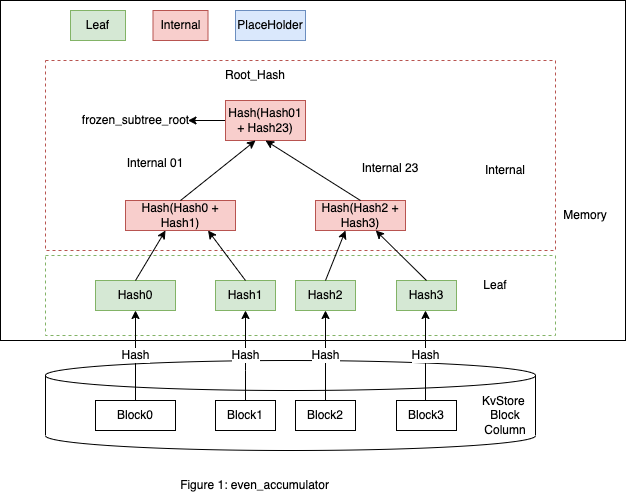
最下面 Leaf 那层的 Hash0 代表 Block0 的 Hash 值,Hash1 代表 Block1 的值,Hash2,Hash3 类似。
这里 Internal01 的左子树是 Hash0,右子树是 Hash1。
Internal 01 的 Hash01 = Hash(Hash0 + Hash1),+ 代表拼接字符串。
在 Accumulator 中 Internal 节点的 Hash 值是由左子树 Hash 值和右子树 Hash 值拼接后再 Hash 计算得出,Hash 计算的函数是 sha3_256。
这里从 Block0 开始是因为在区块链中有创世块(Genesis Block),最上面的根节点叫做 Root_Hash。
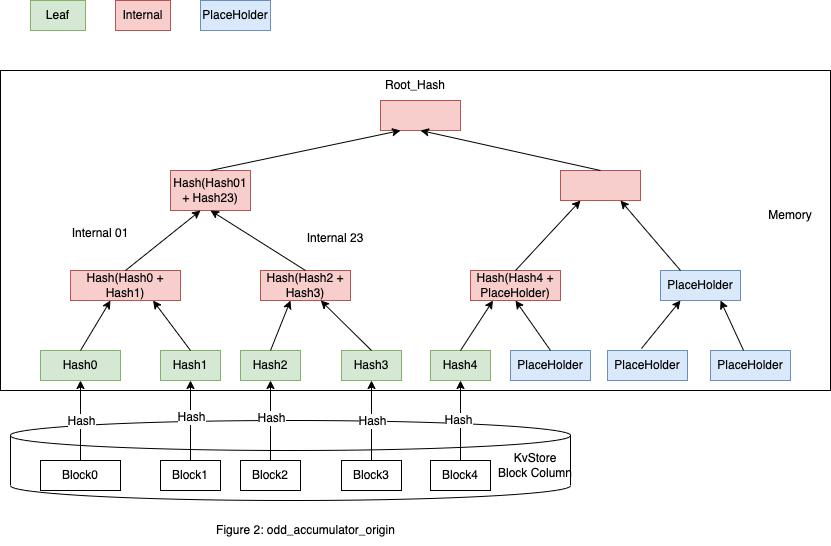
图2显示了奇数个 Block 组成一个 Accumulator 的情况,在图1基础上添加了 Block4,由于 Block4 构建 Internal 需要 Empty 节点来配对,这里 Empty 节点就是 PlaceHolder。
这种情况下要补充多个 PlaceHolder,这里做了些优化,空子树用 PlaceHolder 表示来减少计算,这里 PlaceHolder 有固定的 Hash 值 *ACCUMULATOR_PLACEHOLDER_HASH,如图3。
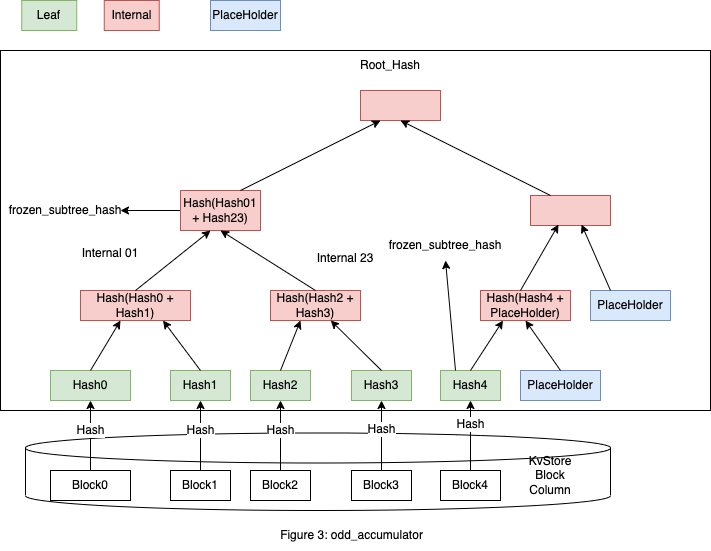
图3中,(Hash(Block), Block) 会按照 Key Value 键值对的形式存在 KvStore 中。
这里给出代码中 Leaf 和 Internal 的定义
pub enum AccumulatorNode {
Internal(InternalNode),
Leaf(LeafNode),
Empty,
}
pub struct InternalNode {
index: NodeIndex,
left: HashValue,
right: HashValue,
is_frozen: bool,
}
pub struct LeafNode {
index: NodeIndex,
hash: HashValue,
}
这里 index 和 is_frozen 在 Internal 和 Leaf 中都不参与 Hash 计算, NodeIndex 主要用途是 Accumulator 存储在 KvStore 中计算 Internal 用到,后面会介绍。
节点的Frozen
Merkle Tree 是在内存中的形式, Accumulator 需要把 Merkle Tree 保存在 KvStore 中。
一种直观的想法就是把所有的 Leaf 节点保存下来,比如图3中,保存 Hash0,Hash1, Hash2, Hash3, Hash4,还需要保存这些顺序关系。
第一次用的时候计算就可以构建 Merkle Tree,图3中需要计算6次,
当 Leaf 数量比较大的时候,比如2^23个 Leaf (大概800万个Block),需要2^23次 sha3_256 计算,这个复杂度是O(N)。
需要加速下计算的过程,注意到 Accumulator 是只添加 Leaf 不会出现删除和更新Leaf的情况,
比如在图3中,Hash0,Hash1,Hash2,Hash3 构建成的子 Accumulator 是 Hash(Hash01 + Hash23), 再添加新的 Leaf,不会修改根节点 Hash(Hash01 + Hash23) 的 Accumulator。
可以基于这些已经固定的子 Accumulator 进行加速计算。可以发现固定的子 Accumulator 都是满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)。
这里引入了 Frozen 的概念。
PlaceHolder 是 not Frozen 的,Leaf 都是 Frozen 的,Internal 的 Frozen 是递归定义,是指左子树和右子树中不含有 PlaceHolder 节点。 一个 Accumulator 中节点数目指所有 Frozen 的节点,在图1中是7个,图3中是8个。 一个 Accumulator 可以通过 Root_Hash 和 frozen_subtree_roots 快速确定下来。 这里定义了 AccumulatorInfo,如下所示:
pub struct AccumulatorInfo {
/// Accumulator root hash
pub accumulator_root: HashValue,
/// Frozen subtree roots of this accumulator.
pub frozen_subtree_roots: Vec<HashValue>,
/// The total number of leaves in this accumulator.
pub num_leaves: u64,
/// The total number of nodes in this accumulator.
pub num_nodes: u64,
}
在图1中 frozen_subtree_roots 元素只有一个就是 Root_Hash ( accumulator_root )。
图3中有2个都标出来了,他们和 Root_Hash 不同。
这里 frozen_subtree_roots 最多只有64个。
原因如下,假设有n个节点,假设 2^k <= n < 2^(k + 1), 第一个 frozen_subtree 用的节点数是2^k,第二个的 frozen_subtree 用的节点数是 2^k1,
其中 2^k1 <= (n - 2^k) < 2^(k1 + 1), 可以发现 frozen_subtree_roots 和 n 的二进制表示中的1是对应的,由于 n 定以为64位整数,最多有64个节点数。
HashValue 使用 sha3_256 计算占 32 个字节,一个 AccumulatorInfo 占的内存最大是(1 + 64 + 2) * 32个字节。
Leaf Index 和 Node Index
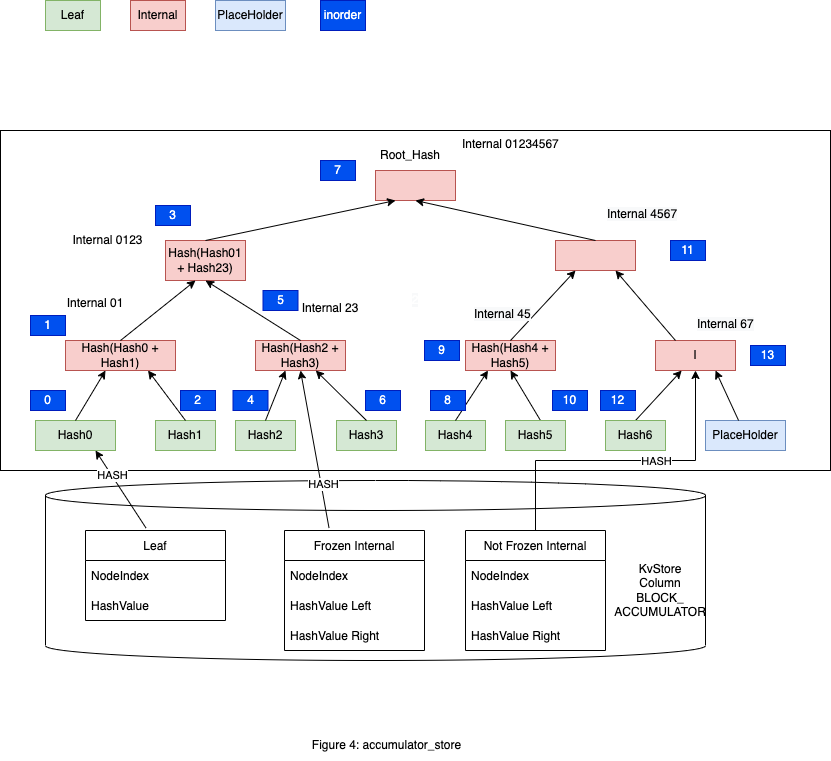
如图1中,Hash0、Hash1、Hash2 和 Hash3 是 Merkle Tree 的叶子节点,他们分别对应 0-3 的叶子节点(计数从0开始)
Leaf Index 就是从左开始叶子节点的顺序。Node Index 是中序遍历 Tree 的各个节点的顺序,Hash0~Hash3 对应的 Node Index 是0,2,4,6。
简略图如下
3
/ \
/ \
1 5 <-[Node Index, in order transver]
/ \ / \
0 2 4 6
0 1 2 3 <[Leaf Index]
Node Index 在代码中表示为 NodeIndex 。 这里使用中序遍历的原因可能是 Accumulator 需要将 Merkle Tree 保存到 KvStore 中,由于保存的都是 HashValue,需要知道 HashValue 在 Merkle Tree 中的位置 图3在图1基础上添加一个 Hash4 的节点,中序遍历情况下各个节点的 NodeIndex 值是不变的。
下面介绍下 Accumulator 的一些操作过程
Accumulator append 过程
pub fn append(&mut self, new_leaves: &[HashValue]) -> Result<HashValue>
上面是对应的代码
 流程分为节点的添加和根节点的计算
流程分为节点的添加和根节点的计算
新节点添加
如图4中,Hash0~Hash3 构建的 Accumulator 的 Root_Hash 为 Hash(Internal0123), 现在添加 Hash4~Hash6。
添加 Hash4 LeafNode,Hash4 添加到 to_freeze,to_freeze = [Hash4],Hash4 为左孩子节点,Hash4 添加完成。
添加 Hash5 LeafNode,Hash5 添加到 to_freeze,to_freeze = [Hash4, Hash5],Hash5 为右孩子节点,需要和其兄弟节点( sibling )生成一个 Frozen 的 Internal 45,
并且添加到 to_freeze,to_freeze = [Hash4, Hash5, Internal45], 这里产生了一个查询 sibling 操作,后面会介绍,Hash5 添加完成。
添加 Hash6 LeafNode,Hash6 添加到 to_freeze,to_freeze = [Hash4, Hash5, Internal45, Hash6],Hash6 为一个左孩子节点,Hash6 添加完成。
根节点的计算
根节点的计算会需要用到 NodeIndex, HashValue 的映射,就是下面提到 index_cache。
需要计算下生成的新 Root_Hash 值,Hash6 和 PlaceHolder 生成 Not Frozen Node Internal67,添加到 not_freeze,not_freeze = [Internal67],
Internal67 和其 sibling 节点 Internal45(这里会产生查询操作)生成 Not Frozen Node Internal4567 添加到 not_freeze,not_freeze = [Internal67, Internal4567],这里会有个查询节点操作,
Internal4567 和其 sibling 节点 Internal0123(这里会产生查询操作)生成一个 Not Frozen Node Internal01234567,
添加到 not_freeze,not_freeze = [Internal67, Internal4567, Internal01234567],Hash(Internal01234567)是新的 Root_Hash。
Starcoin实现中会将 to_freeze 和 not_freeze 合并起来,并构建LruCache<NodeIndex, HashValue>,这个称为 index_cache,查询中会用到
图4中 NodeIndex 用蓝色表示。
index_cache = [(8, Hash4), (10, Hash5), (9, Hash45), (13, Hash(Internal67)), (11, Hash(Internal4567)), (7, HashInternal(Internal01234567))]。
Accumulator flush 和 Accumulator 在 KvStore 中的存储
pub fn flush(&mut self) -> Result<()>
将 append 过程中产生的 to_freeze 和 not_free 合并后按照 (Hash(Node), encode(Node)) Key Value 键值对形式存储在 KvStore 中。
在图4中使用的是 Column BLOCK_ACCUMULATOR,实际还有 Transaction 对应的 Column TRANSACTION_ACCUMULATOR,图中只画了部分 Leaf,Internal。
注意到 Internal 分为 Frozen 和 Not Frozen,图4中 Internal 67这个 Internal 节点是 Not Frozen 的,如果再添加一个新的 Leaf Hash7 会变成 Frozen, 这样会保存
两个不同状态的 Internal67 到 KvStore。
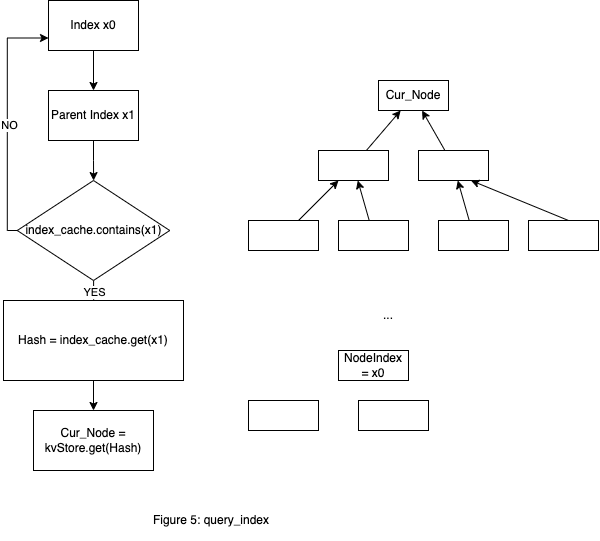
查询操作
fn get_node_hash_always(&mut self, index: NodeIndex) -> Result<HashValue>
这是个 private 操作,主要用在 append 流程中,通过 NodeIndex 查找对应的 HashValue。
Accumulator 在 KvStore 中的存储中提到,Column BLOCK_ACCUMULATOR 保存是按照 (Hash(Node),encode(Node)) Key Value 键值对存储在 KvStore 中,只能从其父类节点一层层查找。
比如查询 NodeIndex x0(假设为2)的 HashValue,查 NodeIndex x1(假设为1)的父节点,如果 index_cache 中有,通过其 HashValue 从 KvStore 中获取这个 Node。
如果 index_cache 中没有,找其父节点的父节点,最终肯定能找到(最差的情况是找到 Root_Hash), 这个节点记为 Cur_Node , 然后再从 Cur_Node 层次遍历找到子孙节点中 NodeIndex 等于 x0 的节点。
流程图见图5
Accumulator 的幂等性
在 Merkle Tree 中提到记住 Root_Hash 就可以认为是记住了整棵树, 在 Starcoin 中,需要保证 Accumulator 是幂等的。 比如在图3中,我们已经执行了 Block0-4 的计算,这时候又有逻辑把 Block4 添加进来计算,这时候会不会出现添加 Block5 实际是 Block4 的逻辑,实际上不会,由于 Block 的 BlockHeader 存储了前一个 Block 的 Hash 值, 通过前一个 Hash 值就知道整个 Accumulator 的 Leaf 数目为4,对应的子 Accumulator 的 Hash 值是 Hash(Hash01 + Hash23),会和 Hash(Block4) 计算新的 Accumulator,这部分需要结合区块执行来理解。
Accumulator 中API说明
创建 Accumulator
pub struct MerkleAccumulator {
tree: Mutex<AccumulatorTree>,
}
impl MerkleAccumulator {
pub fn new_with_info(
acc_info: AccumulatorInfo,
node_store: Arc<dyn AccumulatorTreeStore>,
) -> Self;
}
new_with_info 通过 AccumulatorInfo 创建新的 Accumulator
添加新的元素
fn append(&self, leaves: &[HashValue]) -> Result<HashValue>
添加新的 LeafNode,这个前面介绍过
保存树到 KvStore
fn flush(&self) -> Result<()>;
将 append 产生的新元素存到 KvStore
获取叶子节点
fn get_leaf(&self, leaf_index: u64) -> Result<Option<HashValue>>;
fn get_leaves(&self, start_index: u64, reverse: bool, max_size: u64) -> Result<Vec<HashValue>>;
第一个是获取叶子节点,第二个是批量获取叶子节点
获取proof
fn get_proof(&self, leaf_index: u64) -> Result<Option<AccumulatorProof>> {
获取Merkle Proof证明
其他琐碎细节
append 过程中的获取 frozen_subtree_roots
FrozenSubTreeIterator::new(self.num_leaves)
这里是因为 frozen_subtree 和 num_leaves 二进制里的的1对应, 就是找 MSB 操作(most significant set bit of a u64),原理参考 Hackers Delight 的 flp 部分
NodeIndex 相关操作
如果不想研究 NodeIndex 源码,这部分可以不看 NodeIndex 提供了一些操作 (1)通过 LeafCount 计算整个树高 (2)Leaf Index 和 NodeIndex 的转换 (3)获取左子树和右子树 NodeIndex (4)确定某个 NodeIndex 是否为 PlaceHolder (5)获取父节点的 NodeIndex 这部分细节待添加。
相关资源draw.io
总结
默克尔累加器 MerkleAccumulator 是 Starcoin 区块链另一个核心数据结构,用于提供区块和交易的证明。它的结构如图所示:
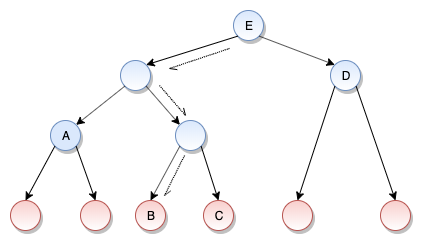
MerkleAccumulator 是一个叶子节点可以从左到右不断增加,从而不断累加的默克尔累加器。
Starcoin 区块链设计了两个默克尔累加器,分别是区块默克尔累加器和交易默克尔累加器。 上图红圈表示叶子节点,对应区块默克尔累加器就是指区块,对应交易默克尔累加器就是指交易;蓝圈表示中间节点。 所以 Starcoin 区块链可以非常方便的给区块或者交易提供证明,例如,上图中叶子节点 B 的 Proof 是 CAD。